Calibration Services
AAW can provide UKAS Accredited and UKAS Traceable calibrations for monitoring systems within the food production, medical and pharmaceutical industry
Completing a calibration at two or more set temperatures allows the sensor accuracy to be tested across the whole the expected temperature range. Sometimes a sensor can show a greater error at a lower temperature compared to a higher temperature and vice versa.
A multiple point calibration allows us to calculate an offset that is more accurate and ensures that any error the sensor has remains equal at both high and low temperatures.
Calibration Quotes
Calibration Reports
AAW Engineers can calibrate sensors in house or on site dependent on your requirements.
An engineer carrying out an onsite calibration can produce a turnaround of 40+ sensors per day, with minimal disturbance to your normal working procedures and environment.
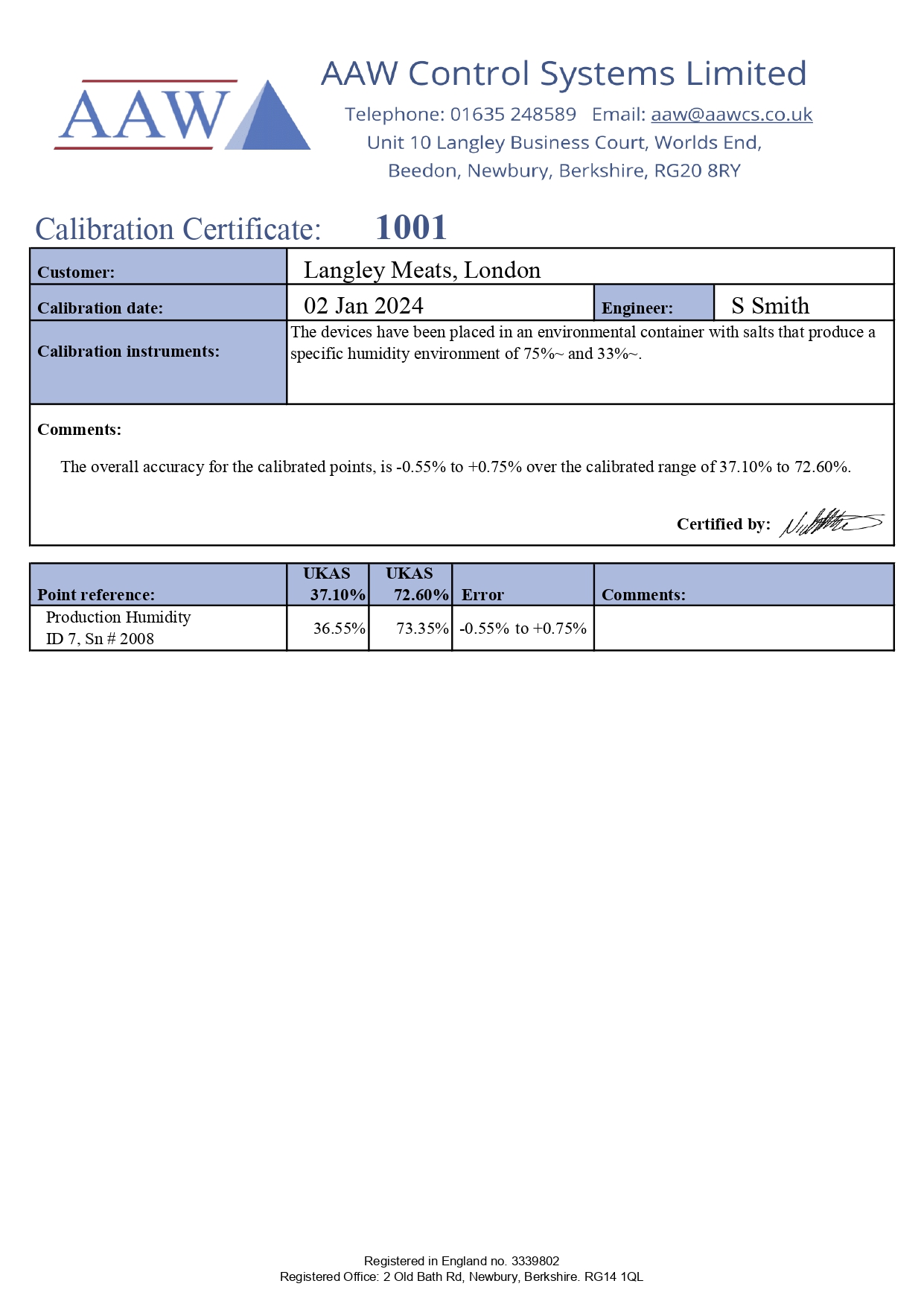
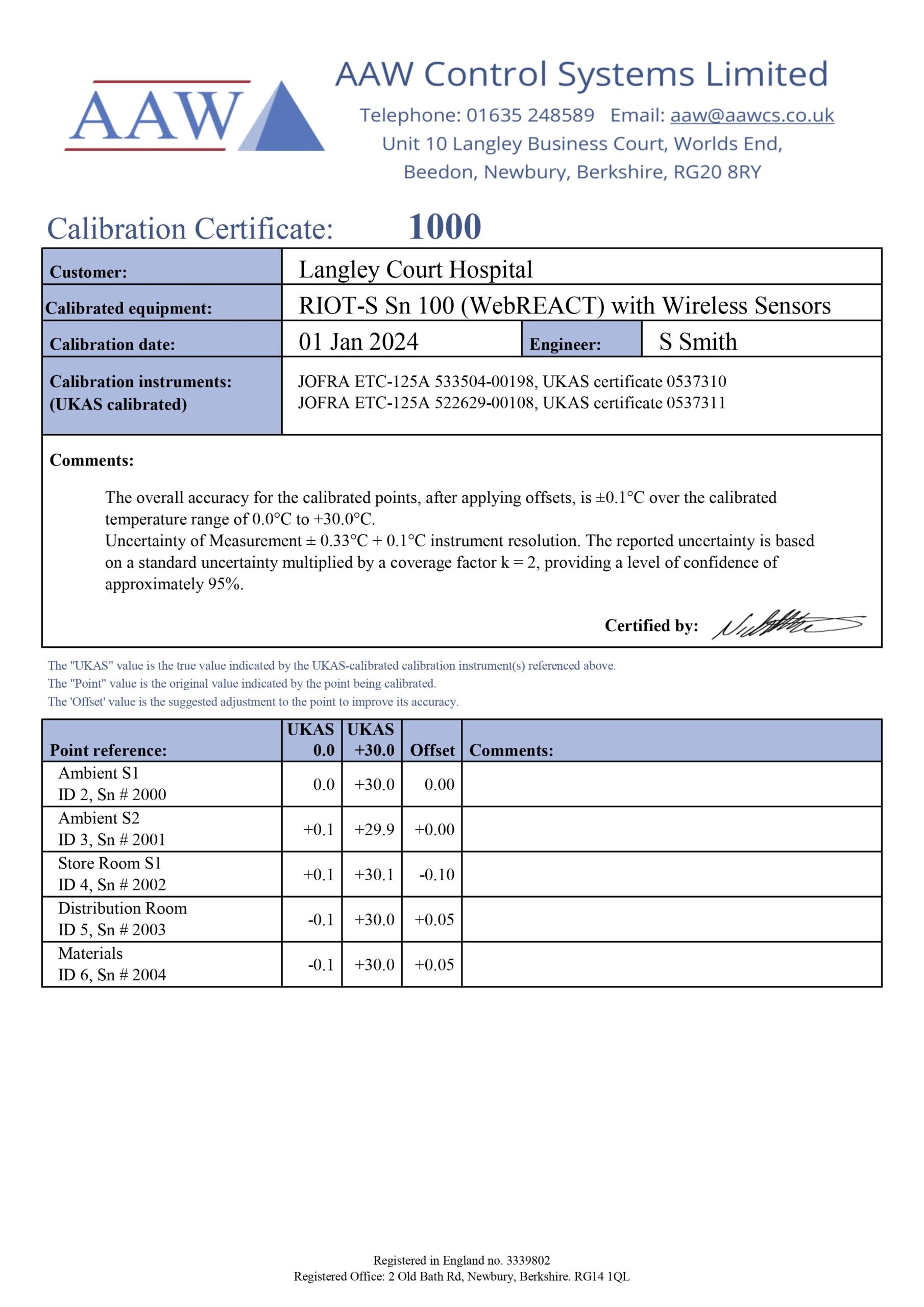
Please find examples of calibration certificates to the right. PDF copies of your calibration reports would be emailed to you. If you have a WebREACT site hosted by AAW, we will upload the results to your site so you can view them at anytime.
ERROR
Error is the difference recorded between the measurement device and the sensor that is being calibrated.
Example: The Measurement Device gives a value of +5.0°C and your temperature sensor value is +4.9°C.
Therefore the Error of your sensor is -0.1°C
-0.1°C is how far your sensor has deviated from being accurate.
DRIFT
The values read by a temperature sensor can drift and the accuracy of the readings will in decrease. Sensor drift is common and can happen slowly. There are various causes such as: environment, vibration, pressure & temperature fluctuations.
It is common for temperature sensors drift over time and can be managed with annual calibrations and offsets, eventually replacing the sensor will be necessary when calibrating out the error is no longer possible.
OFFSET
The offset is the value you would to apply to a sensor to see no difference against a measurement device value.
It is the inverted error value; using the example above the error is -0.1°C, therefore the sensor would require an offset of +0.1°C to align the sensor with the measurement device.
For sensors that are calibrated at multiple set temperate points; the offset is calculated using all the errors from that calibration and also factors in the operational/running temperature of the sensor location.
Example: A sensor is monitoring an environment that averages +5.0°C.
The sensor reads the following calibration results:
Measurement Device: -5.0°C, Sensor: -4.9°C, Error -0.1°C
Measurement Device+5.0°C, Sensor: +5.0°C, Error 0.0°C
No offset would be applied as the sensor is most accurate at the running temperature of the location it is monitoring.